Almonds have been prized since ancient times as one of humankind’s most beloved
nuts. They
were popular in the diets of ancient Egyptians and Indian populations.
Ancient Indian Ayurvedic practitioners even believed that almonds were
capable of increasing brain capacity, intellectual ability and
longevity.
Today, almonds nutrition benefits are praised around the world, and they are used in numerous different ways: eaten raw as a
healthy snack; as the base ingredient in almond butter, almond milk or almond flour; and even in many body lotions and fragrances.
Cholesterol reduction
is the most celebrated health benefit of almonds, but there are many
other vital health benefits of almonds nutrition. Almonds are low in
saturated fatty acids, rich in unsaturated fatty acids, and contain
filling fiber, unique and protective phytosterol
antioxidants as well as plant protein.
And don’t fear the fat in almonds — almonds are actually beneficial
when it comes to losing weight, despite their higher calorie content.
One study even found that almonds consumed as snacks reduce hunger and
desire to eat later in the day, and when dieters eat almonds daily they
reduce their overall calorie intake.
(1)
Almonds Nutrition: The Facts Behind the Benefits
Botanically, almonds (scientifically termed
Prunus dulcis) are
actually very small stone fruits in the Amygdalus family and related to
other fruits that contain hard pits, including cherries, plums and
peaches. Almonds are a type of drupe nut, which means along with other
nuts like macadamias, pecans and walnuts, they have multiple layers that
enclose a single, hard seed in the center.
Almonds are considered dry drupes so they first must be extracted
(which is called “shelling”) before being sold and eaten, which is why
you might see the description “shelled almonds” when you purchase
ready-to-eat almonds.
In the medical world, almonds nutrition is most praised due to the presence of monounsaturated fatty acids, dietary
fiber, antioxidants, vitamins like
riboflavin, and trace minerals such as magnesium. (
2)
Although almonds are high in calories and considered “energy-dense”
(as all nuts are), they provide a whole range of critical nutrients and
chemical compounds that often lack in the standard American diet
(sometimes called “SAD”).
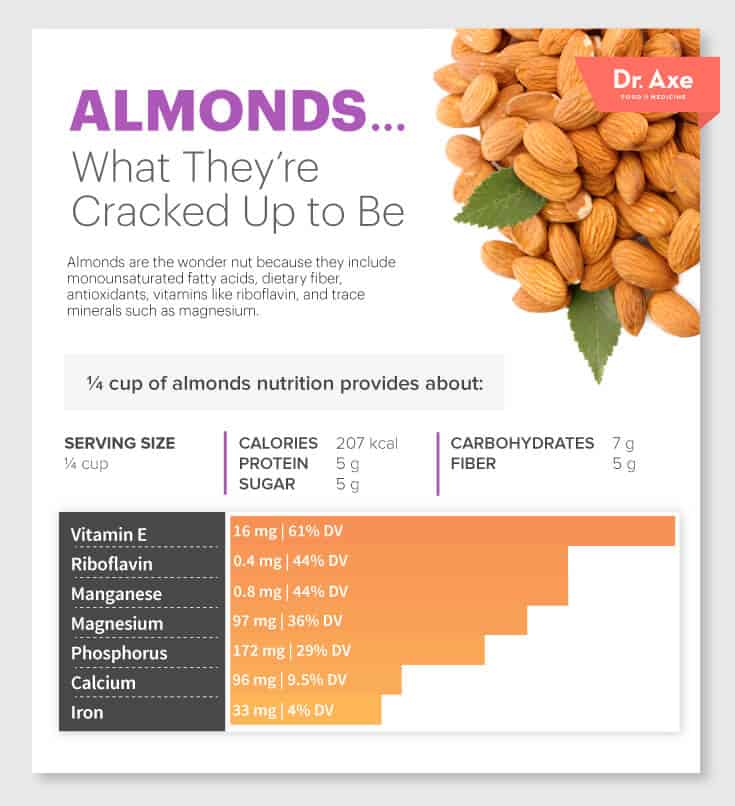
¼ cup of almonds nutrition provides about: (
3)
- 207 calories
- 5 grams of protein
- 5 grams fiber
- 7 grams of carbohydrates
- 5 grams of sugar
- 16 milligrams vitamin E (61 percent DV)
- 0.4 milligrams riboflavin (44 percent DV)
- 0.8 milligrams manganese (44 percent DV)
- 97 milligrams magnesium (36 percent DV)
- 172 milligrams phosphorus (29 percent DV)
- 96 milligrams calcium (9.5 percent DV)
- 33 milligrams iron (4 percent DV)
9 Proven Health Benefits of Almonds
1. Help Prevent Heart Disease and Heart Attacks
Two of the star chemical compounds of almonds nutrition are healthy
monounsaturated fatty acids (abbreviated as MUFAs, the same kind of
beneficial fat found in olive oil) and antioxidants that support
heart health
and prevent factors of cardiovascular disease. Almonds specifically
supply antioxidant flavonoids, plant-based compounds present in the skin
of almonds that work with vitamin E to improve artery health and reduce
inflammation.
Almonds nutrition also holds key nutrients to heart health, including
arginine, magnesium, copper, manganese, calcium and potassium. Studies
show almonds have a consistent “bad” LDL cholesterol-lowering effect,
especially in individuals with high cholesterol and diabetes. (
4)
Almonds help prevent damage from forming within artery walls
and protect against dangerous plaque buildup. Almonds nutrition benefits
also make them a great food to support healthy cholesterol and blood
pressure levels, in addition to fighting weight gain and obesity — three
of the biggest risk factors associated with heart attacks and stroke.
2. Support Healthy Brain Function
Almonds are often considered one of the best
brain foods.
Almonds nutrition is somewhat unique in that almonds contain riboflavin
and L-carnitine, two key nutrients capable of positively affecting
neurological activity and preventing cognitive decline. This is one
reason why adults, especially the elderly, are encouraged to eat nuts
several times per week — since they are associated with a reduction in
the risk for inflammation that can cause brain disorders including
dementia and
Alzheimer’s disease.
3. Maintain Skin Health
Almonds are a great source of
vitamin E
and other antioxidants that nourish the skin and reduce signs of aging.
Research finds that almonds nutrition contains high concentrations of
catechin, epicatechin and flavonol antioxidants, including quercetin,
kaempferol and isorhamnetin — compounds that fight
skin cancer and damage by reversing oxidative stress from a poor diet, pollution and UV light exposure. (
5) Almonds’ healthy fats, plus their ability to improve circulation, also help keep skin hydrated and better able to heal wounds.
4. Help Control Blood Sugar Levels and Prevent Diabetes
Almonds’ rich supply of MUFAs helps slow the rate at which glucose
(sugar) is released into the bloodstream. In addition to managing blood
sugar and preventing insulin resistance (which can occur over time when
the body becomes less reactive to insulin, the sugar-controlling
hormone), almonds nutrition benefits include the ability to lower other
common diabetes risks: unhealthy body weight,
inflammation and high levels of oxidative stress.
5. Help With Weight Loss and Prevent Overeating
Healthy fats and dietary fiber aid in
weight loss
because they help you feel full, which curbs overeating and unhealthy
snacking. Although nuts are high in fat and calories, they prolong the
feeling of satisfaction after you eat and keep your blood sugar more
stable than low-fat meals do. Thus, you’re less likely to experience a
roller-coaster of energy dips and food cravings.
Studies, such as the Nurses’ Health Study, even show that almonds support a healthy
metabolism.
Also, people who frequently eat almonds and other nuts retain healthier
body weights and lower rates of obesity over time compared to those who
avoid nuts. Other studies show that when dieters eat almonds daily,
they are less likely to overconsume carbohydrates and more likely to
reach and maintain a healthier body weight. (
6)
For example, one 2003 article published in the International Journal
of Obesity found that when women consumed almonds over a six-month
period, compared to other women who didn’t eat almonds, they experienced
greater reductions in weight/BMI, waist circumference, fat mass and
systolic blood pressure.
6. Increase Nutrient Absorption
The body needs adequate amounts of fat in the diet in order to properly absorb “fat-soluble” nutrients, like
vitamins A
and D. Almonds are also considered one of the only nuts that help
alkalize the digestive tract, reducing acid buildup and balancing the
body’s pH. A healthy
pH level is
crucial for proper digestion, immunity and disease prevention.
Additionally, the nutrients present in almonds may help regulate
digestive enzymes that are involved in nutrient extraction, cholesterol
synthesis and bile acid production.
7. Increase Digestive Health
In addition to healthy fats and alkaline-forming molecules, almonds
(especially the skin of almonds) contain probiotic components that help
with digestion,
detoxification
and healthy bacterial growth within the gut flora — a key to actually
utilizing nutrients from food and preventing nutrient deficiencies.
Studies suggest that almonds and almond skins may lead to an
improvement in the “intestinal microbiota profile,” meaning the
intestine’s bacterial activities improve and promote numerous health
benefits due to the presence of prebiotic properties, the precursors for
probiotics.
A 2014 study by the Institute of Food Science & Technology in
China found that when women ate a daily dose of 56 grams of almonds over
an eight-week period, significant increases in the populations of
healthy bacteria called Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus were observed.
(
7)
8. Can Help Fight Cancer and Inflammation
Almonds contain gamma-tocopherol, a type of vitamin E that acts as a powerful antioxidant, fighting
free radical damage and oxidative stress that are linked to
cancer.
Many studies find a link between nut consumption and cancer prevention,
including a reduced risk for colon, prostate and breast cancers. (
8)
9. Help Maintain Dental and Bone Health
Almonds are a good source of trace minerals, including magnesium and
phosphorus, which is a crucial nutrient for building and maintaining
strong teeth and
bones. Almonds nutrition benefits include the ability to help prevent
tooth decay, fight cavities, lower the risk for bone fractures and fight osteoporosis.
Almonds History and Interesting Facts
Would you believe that today the almond industry is estimated at $4.3
billion annually and over 2 billion pounds of almonds are produced
worldwide each year? Unlike many other nuts and fruits, the U.S. —
specifically California, which is actually the only state to produce
almonds commercially — is the largest producer of almonds, producing
about 80 percent of the world’s almonds.
Almonds might be growing in popularity every year as research reveals
more about almonds nutrition benefits, but almond consumption actually
goes back thousands of years to around 4,000 B.C. The almond tree
species is native to the Middle East and South Asia. A tall tree with
pink and white flowers, it grows in warm and dry climates, which is why
it spread through the Mediterranean region and became a staple in the
diet there.
Wild almonds are actually bitter and naturally contain toxic
substances like deadly cyanide, so humans had to first find a certain
type of “sweet” almond among the many different almond tree species
before domesticating them. In India and Pakistan, almonds have been a
mainstream part of the diet for centuries, where they’re called
badam.
Almonds were first spread by humans in ancient times along the shores
of the Mediterranean into northern Africa, Asia and southern Europe,
eventually making their way to the U.S. Along the way, the word “almond”
was given to the nut, which comes from the old French word
almande.
Historically, almonds have meant many things to various cultures.
Hebrew literature from 2,000 B.C. mentions almonds, as does early
literature from Turkey, Romania and the Baltic peninsula. The Bible also
makes numerous references to almonds, describing them as an object of
value and a symbol of hope, for example, in Genesis 43:11.
King Tut also took several handfuls of almonds to his grave dating
back to 1352 B.C., and years later almond trees were believed to grow
near trade routes like the famous Silk Road that connected central China
with the Mediterranean.
How to Buy and Use Almonds
Not all almonds are created equal — you definitely want to avoid
almonds and any nuts coated in sugar, hydrogenated oils and tons of
sodium. Many nuts undergo processing that lower the nut’s health
benefits. For example, by heating nuts to very high temperatures, some
of their antioxidants can be destroyed.
One downside of consuming almonds produced in the U.S. is that United
States law demands that all raw almonds be pasteurized or irradiated
before being sold to consumers. According to the Department of
Agriculture (USDA), there are several mandatory pasteurization treatment
processes to reduce the level of potential contamination in almonds
“without diminishing the product’s quality, nutritional value or sensory
qualities (taste and crunch).” (
9) These include: oil roasting, dry roasting and blanching, and steam processing.
Almonds contain natural fatty acids and oils that are sensitive to
high heat, so when they’re highly processed it’s possible to turn these
oils “rancid.” For example, when almonds are roasted, they’re usually
soaked in hydrogenated or
GMO oils, a fat that’s harmful and promotes heart disease.
As a rule of thumb, the less processing done to almonds the better.
Preshelled and roasted almonds are likely less beneficial than raw
almonds still found in their natural casing.
One step that can actually increase the nutrient content of almonds is soaking and
sprouting them. Soaking and sprouting almonds removes some of their naturally occurring
antinutrients
that block the body from absorbing some minerals. I like to soak mine
overnight for 12–24 hours in a big bowl, covering them with water and
rinsing them the next morning.
Almonds come in two varieties: sweet and bitter. Sweet almonds are
used in many recipes in Asia, the U.S. and the Mediterranean. One
popular use in Italy is to crush almonds into marzipan, which is used as
a sweet ingredient in baked goods. They’re also added to stir fries,
used to make almond oil for cooking and produce almond extract that
makes a good stand-in for vanilla extract.
Additionally, oils from sweet almonds are extracted to form almond
essential oil, a beneficial oil with many healing body and household
uses.
How About Almond Butter or Almond Flour?
Both are great options for adding more almonds nutrition into your
diet. Almond butter is simply ground almonds, but look for butters that
contain no added oils or sugar. Your best bet? Make almonds yourself by
grinding them in a high-speed blender or food processor until smooth.
When it comes to almond flour (also called almond meal), again look
for simple and straightforward ingredients, usually just almonds. Use
almond meal to replace bread crumbs, and combine it with other
gluten-free flours or
coconut flour to make baked goods.
Recipes Featuring the Almond!
Total Time: 25 minutes
Serves: 9
INGREDIENTS:
- 2 cups steel cut oats
- 4 scoops vanilla whey protein powder (1 cup)
- ¼ cup oat flour
- 1 tablespoon flaxseed, ground
- 1 cup sprouted almond butter
- ¼ cup honey
- 2 ripe bananas
- ½ cup applesauce
- 1 teaspoon vanilla Extract
DIRECTIONS:
- Preheat oven to 350 degrees F.
- Grease 8×8 pan with coconut oil.
- Mix the oats, whey, oat flour and flaxseed. Once combined, add almond butter, applesauce, vanilla and honey.
- Mash the bananas into the mixture and combine.
- Spread batter into pan and bake about 15 minutes.
You can also take advantage of almonds nutrition by making some of these healthy and easy recipes:
- Almond Berry Cereal Recipe —
Conventional cereal can be full of refined sugar! Instead, try this
almond berry cereal recipe. It’s full of healthy fats to help support
hormone health and give energy throughout your day.
- Dark Chocolate Almond Butter Recipe — This recipe is an amazing addition to any snack. Try this fun twist on a classic and enjoy.
- Coconut Almond Joy’s Recipe — Coconut is another one of the healthiest foods you can eat. Coconut
is a medium chain fatty acid that is easily digested and converted to
energy instead of being stored as fat. Thus, coconuts can aid in weight
loss, help stimulate the metabolism and have amazing antimicrobial
properties.
Are There Possible Side Effects of Consuming Almonds?
As with all nuts, allergies can be an issue for some people when it comes to almonds. Children are more susceptible to nut
allergies and should avoid almonds if they have a known allergy.
For those not allergic almonds, there are a few other potential
downsides to almonds when eaten in large amounts — mainly that they
provide a high amount of calories and too much
vitamin E
in some cases. Eating too many nuts can trigger weight gain, cause
certain medicine interactions (like vitamin E overdose) and might lead
to gastrointestinal problems in some, but this is usually only a risk if
you consume a very high amount. As with all sources of healthy fats,
they should make up a substantial part of your diet, but portion control
is important.
One final note is that raw almonds have the potential to carry
bacteria, which is why the USDA requires them to be processed. In rare
cases, salmonella and e-coli have been carried by raw almonds, so as of
2007, raw, untreated California almonds aren’t technically available in
the U.S. — although most people experience no problems eating raw
almonds.
When it comes to bitter almonds, according to the FDA, bitter almonds
are considered “poisonous” since they contain certain acids that can
cause problems in rare cases, so they aren’t recommended for consumption
— although some alternative health practitioners disagree with this.
Don’t let the side effects scare you. Almonds nutrition is extremely
beneficial for your health! And they’re so many uses for tasty treats
and a healthy diet. Incorporate almonds nutrition into your diet today
and see the benefits firsthand!
From the sound of it, you might think leaky gut only affects the
digestive system, but in reality it can affect more. Because Leaky Gut
is so common, and such an enigma, I’m offering a free webinar on all
things leaky gut.
Click here to learn more about the webinar.Source: https://draxe.com/almonds-nutrition/